Few things are more important in business today than data. Technology has empowered companies to collect data on almost every detail of business and measure it in multiple ways. And business success often depends on how well companies collect data, organize it – and back it up.
Without a doubt, having a backup plan for the storage of data is more crucial than ever, but that doesn’t mean it’s a novel concept. The methods by which we store and preserve information have gotten more advanced over time based on the resources that have become available to us. Thanks to information and processes that people began using to preserve data many ages ago, we’ve been able to adapt technology to develop the most reliable and sophisticated systems yet.
To understand why this is important and what you should know about it for your business, let’s briefly look back at the history of data backup.
Data in Industry
Among the milestones in the history of data backup, the Industrial Revolution in the 1800s profoundly accelerated how data could be used in business, and this era quickly created a need to begin to store data reliably.
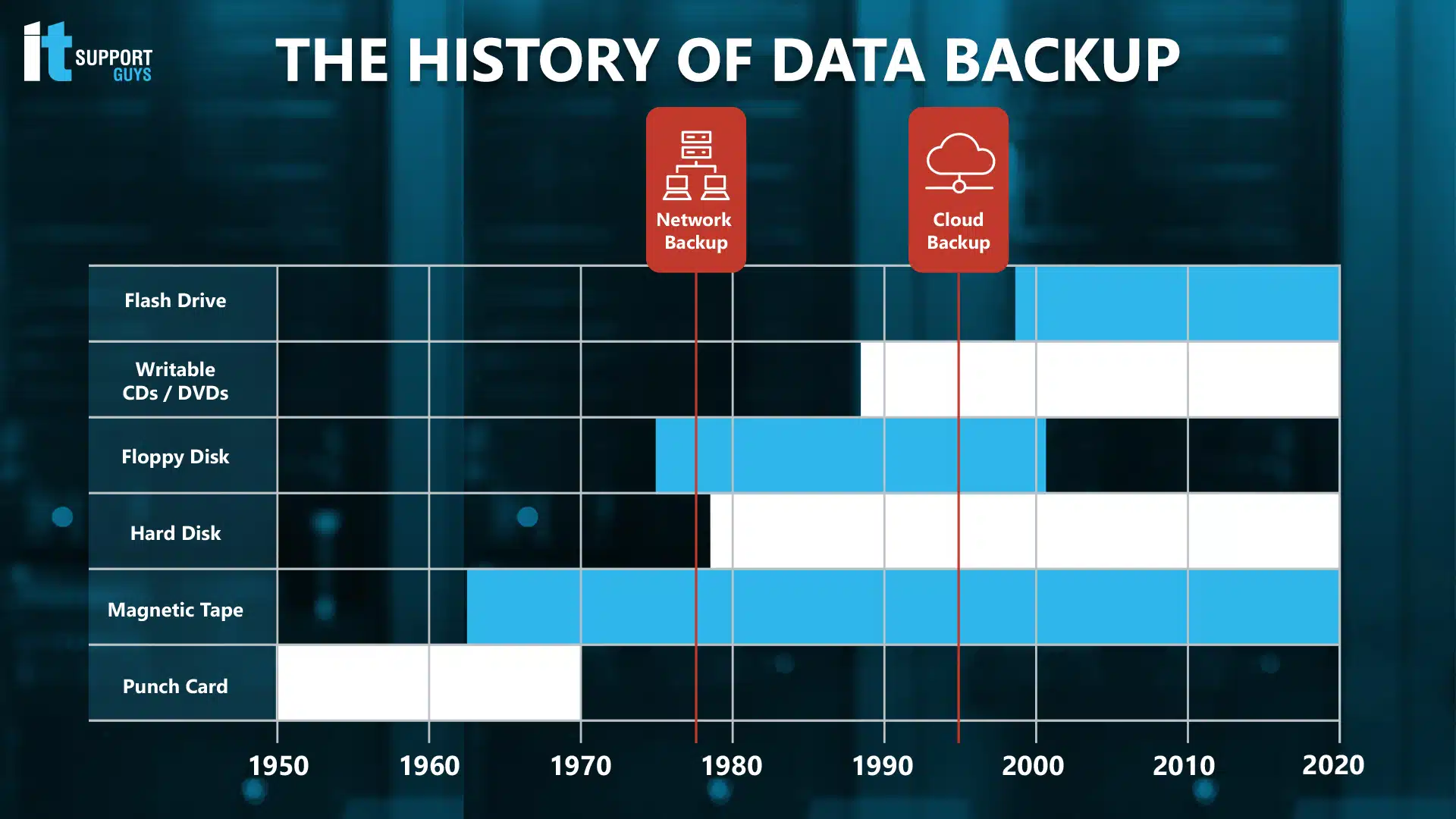
Coming a long way from ancient cave drawings and Egyptian hieroglyphics on papyrus, the punch card technology that emerged with the Industrial Revolution collected and stored vast amounts of data that a newly modernized society needed. Among other developments, punch card technology drove the formation of the Tabulating Machine Company, which was one of the companies that would ultimately merge to become International Business Machines, or IBM. With IBM behind it, punch card technology quickly became the technology of choice for data entry, processing, and storage, and this technology would end up powering everything from time clocks, to voting machines, to general computer programming devices for decades.
But, as with any technology, punch cards had their shortcomings. One was that the cards that were needed for the data to be preserved. Eventually, magnetic tape was developed as an alternative, and backup technology was changed yet again.
Tape Technology Gets on a Roll
By the 1950s, millions of punch cards were being used. It was then that tape was introduced. Each roll of tape could store as much data as what once took 10,000 punch cards to preserve, and it cost much less to process. As a result, tape quickly phased out punch cards, and by the early 1960s, even small businesses were using tape to back up their computer data.
But since tape takes a long time to complete a backup job, backups had to be run when nobody was using the systems. With more and more businesses operating at all hours, this became less and less of a practical option. Plus, tape took a long time when it had to be used to restore data. It could take several hours to restore a single tape, and longer if a business required multiple tapes. When a business became crippled because of a major data loss event, this delay could have a huge impact.
Disk Drives
It wasn’t long after tape drives were developed that IBM also developed the first hard disk drive, or HDD. The first of these was outrageously expensive, costing thousands of dollars for a few megabytes of storage, but it wasn’t long before the technology was incorporated into the massively popular personal computer so that files could be easily stored and accessed.
However, HDDs didn’t replace tape as the popular backup option until the 1990s. Tape remained a more cost-effective option, and HDD still didn’t have a way to connect easily to other systems. Prices, though, continued to drop for hard drives, and their capacity grew. As a result, when transportable media like floppy disks, zip drives, writable CDs/DVDs, and flash drives were developed, the switch to HDD backups suddenly made a lot more sense. Not only were they faster, but software could also set an automated backup to run, preventing incremental data loss.
As a result, most businesses soon began to save their backups on a hard drive, either kept on-site or remotely, safe in a dedicated storage center. This was augmented by the most recent and revolutionary developments to backup technology and data loss mitigation.
The Cloud
The cloud is actually nothing new in technology. It can be summed up as an array of computers that you pay to use and store data on that use broadband internet to transfer data back and forth. When it was first introduced commercially in the mid-1990s, users had a healthy skepticism about the security of their cloud services and data. It was because of this skepticism that many organizations have built in-house cloud storage on their servers or co-located their files to a facility where they had direct responsibility for server management.
As with anything else, though, there are some pros and cons to using cloud technology. Not having to manage hardware saves on expenses and time, a big plus. However, the more data you have, the faster your costs will climb, and despite cloud services typically being a monthly expense, a large enough cache of data in the cloud may not be feasible to maintain.
Backup and Disaster Recovery
This conundrum led to the development of an approach where the history of data backup and security had been heading – a complete backup and disaster recovery (BDR) solution. This two-pronged approach both backs your data up to network-attached storage (NAS) device and an off-site data center. Combining the storage capabilities of both the cloud and the hard drive of the NAS device, a BDR solution can keep multiple copies of your business data ready to help restore your business’s operations should anything disastrous happen.
This history of backup is important to understand when considering some of today’s biggest security threats, especially ransomware attacks. To effectively protect themselves against today’s ransomware threats, businesses must have at least one completely offline, or air-gapped, backup. With an air-gapped backup, a business can retain a malware-proof silo of information that it doesn’t have to worry about.
To ensure both swift business continuity and disaster-proof backups in the future, businesses must find a balance of past and present techniques. While a cloud-based, online backup will prevent physical damage, an air-gapped backup will prevent remote attacks by enabling a company to be fully removed from any network.
Looking Forward
We’ve come a long way from preserving information on physical walls to storing it in hypothetical clouds. Throughout each major period in history, we’ve had critical data that has become lost for different reasons. Now, in today’s business age, the more that we move to a fully digital economy that relies on internet storage, interconnected devices, and automated systems, the greater the instant impact that data loss can have on society.
To this end, now that we have revolutionary new ways to back up data more securely and reliably than ever, and we owe it to ourselves, our businesses, and our customers to take advantage of these approaches and learn from the past by preserving data the best ways we know how.
At IT Support Guys, we understand how critical your data is to your success, and we’re dedicated to helping you protect it. To learn more about how we can help you with a strategy that meets your business’s needs, find out about our backup and disaster recovery services, or reach out to us at 855-448-4897.