Privacy and information security have always been on the front of everyone’s mind. In the past, military leaders would send coded messages through battlefields using cryptography. Today, we share private information, including financial and healthcare information, online. The more we share, the greater the chance of our private information falling into the hands of criminals. Computers today take the same techniques of cryptography for encryption. Learn how encryption is keeping your information secure.
What is Encryption?
Encryption is one of the many ways to secure information that is transferred between users. Where a simple password blocks access to a message or document, encryption takes security a step further. Encryption uses complex algorithms to encrypt, or code, information to the point that it’s unreadable without the use of a key.
The philosophy behind encryption has been around for as long as people have been communicating. Information security has always been a priority for humans, particularly among militaries. To make privacy a reality, cryptography was born. The earliest forms of cryptography would use simple substitution. Letters in a message would be shifted a fixed amount down the alphabet.
A lot has changed since then. While the principles are the same, computers and technology have stepped up encryption to a whole new level.
How Does Encryption Work?
Today’s encryption takes the core foundation of early cryptography and uses advanced algorithms and mathematical equations to encrypt information.
The process starts with a piece of information, for example, an email. After the writer sends out the email, the computer uses a key to encrypt the message. This encrypted message is known as ciphertext. If you looked at ciphertext, it would be a jumbled mess of letter, numbers, and symbols. It would be easy to assume someone fell asleep on their keyboard and that’s what came out.
The email is then received. The recipient’s computer has an identical key as the sender’s computer. This key allows the computer to decipher the message back to a readable form enabling the recipient to read the email.
This is a simple explanation of a complicated process, but sometimes a simple example is all you need.
What Are the Different Types of Encryption?
Encryption can be split up into two types: symmetrical and asymmetrical. The fundamentals of the two types are the same, they both set out to offer secure ways to transmit information. What sets them apart is how they are carried out. So, let’s dig a little deeper into the two types of encryption.
Symmetric
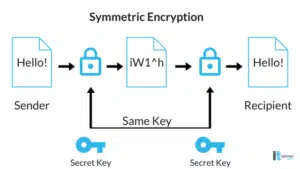
The first type is symmetrical encryption, also referred to as a ‘secret key,’ and is the easier of the two to understand. Symmetrical encryption uses a single key to both code and decipher a message or document. Each computer that receives the information will need a copy of the key. To ensure this, the key is sent with the message inside the code. The computer receiving the message will pick out the key and use it to decipher the contents.
Within symmetrical encryption, there are various versions. The most popular one being the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). AES offers 128, 192, or 256-bit keys, with the 128-bit key totaling 300,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 key combinations. Have fun trying to decipher that by yourself.
Asymmetric
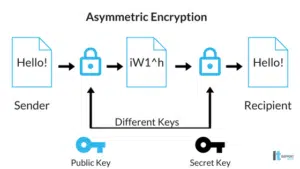
On the opposite end of encryption is asymmetrical, or public key, encryption. The difference between this and symmetrical encryption is that asymmetrical uses two different keys to encrypt information. The first key is the same as symmetrical. It is used to encrypt the message or document shared with everyone. The second key encrypts the symmetrical key. The code to decipher the second key is known only by the computers communicating with each other. The first key is public and known by everyone.
Where Encryption Comes in Handy
Where ever there is information being sent, there is encryption. We mentioned email earlier, but that’s just the beginning.
Online banking and shopping may be the most important use of encryption. It’s what has allowed them to be what they are today. You would be insane if you freely exchanged your bank account information or credit card number with zero security. With encryption, it’s almost second nature.
In business, encryption ensures all collection and transfer of client, customer, and employee information is done so securely.
To improve your business’ encryption practices and overall network security, call IT Support Guys today. Our security tools protect small businesses just like yours every day from security threats big and small. Call 855-4IT-GUYS (855-448-4897) to speak with a specialist and schedule your free network assessment.